Using HPE MapR Data Fabric Storage Container
 About This Lab
About This Lab
Welcome to this Lab on HPE CSI Driver for Kubernetes with MapR Data Fabric Storage and SQL Server 2019 Lab.
Kubernetes allows you to create and manage containers. From a perspective of SQL Server, kubernetes provides:
- A scalable architecture to deploy containerized applications and data platforms such as SQL Server
- Persistent storage for stateful containers like SQL Server
- Built-in load balancers to abstract application connections to SQL Server
- Built-in high availability for stateful containers like SQL Server
- An ecosystem for Operators to simplify application deployment and manage high availability
MapR Data fabric or kubernetes benefits :
- Persist data for containerized applications
- Scale data and performance as containers grow
- Benefit from MapR tickets, for end-to-end security
- Multi-tenant deployment and access
The purpose of this demo is to show you how to use the MapR storage function for SQL Server in a kubernet environment.
 Note: The Kubernete cluster and MapR Data Fabric cluster and CSI driver are already deployed
Note: The Kubernete cluster and MapR Data Fabric cluster and CSI driver are already deployed
 Learning Objectives
Learning Objectives
When you complete this live demo, you will be able to:
- Understand Container Storage Interface (CSI) Driver for Kubernetes
- Know how to install the HPE CSI driver MapR for kubernetes
- Understand Kubernetes deployment
- Understand Dynamic Provisionning , Persitent Storage on Kubernetes
- Understand the basics of deploying SQL Server on an Kubernetes cluster
- Connect and run queries against SQL Server deployed on Kubernetes
 Business Applications of this Lab
Business Applications of this Lab
- Developers looking to deploy a database container for their applications on Kubernetes.
- Database Administrators looking to understand how to deploy database platforms like SQL Server in a Kubernetes cluster using Kubernetes.
 Infrastructure description
Infrastructure description
You’ll need a local systems or Virtual Machines that you are able to install software on.
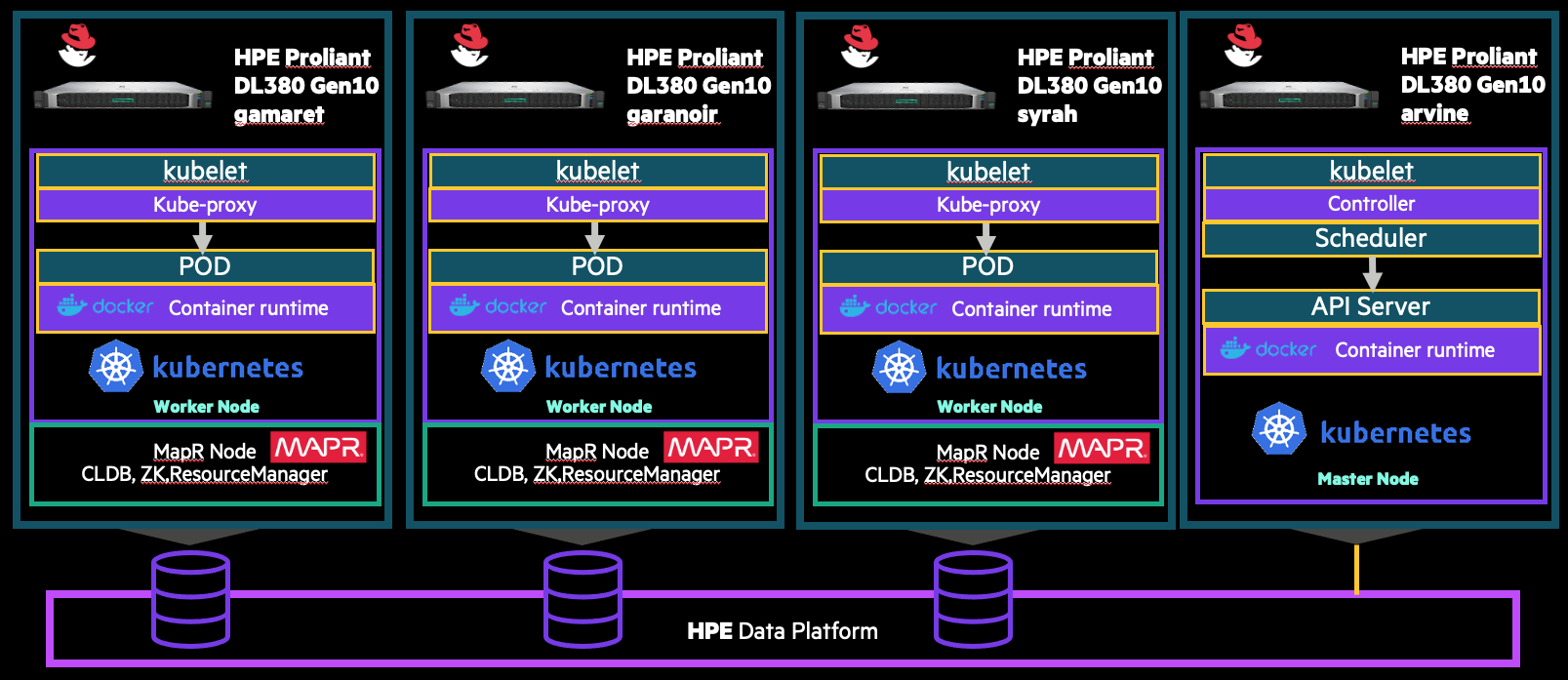
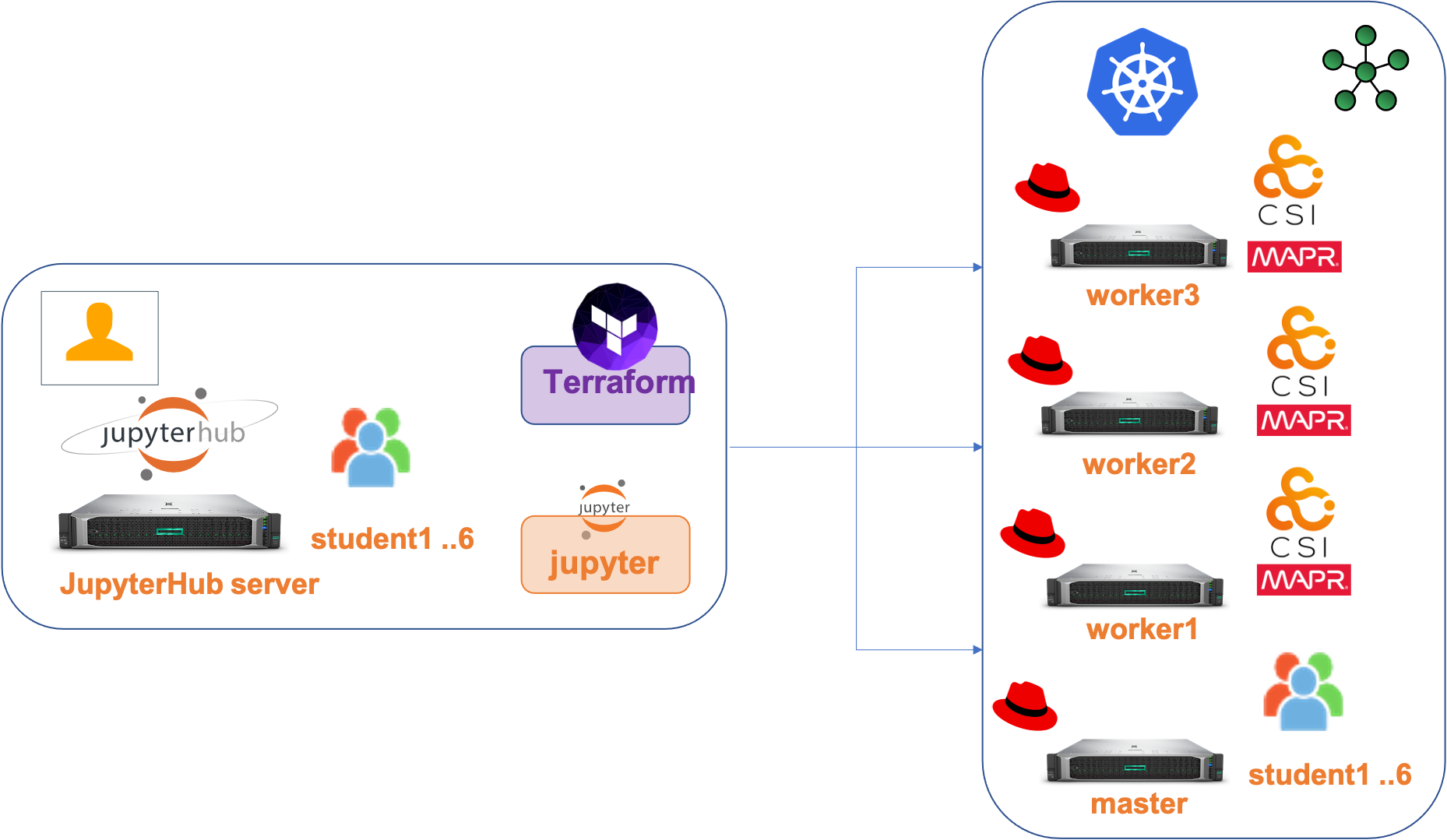
The infrastructure of the platform is composed of:
- 1 Master node : arvine
- 3 Worker nodes : gamaret, garonoir, syrah
- 1 MapR Data Fabric cluster 6.2 with 3 nodes , the same nodes for kubernetes cluster
- Microsoft SQL Server 2019 container
- RedHat Enterprise server 8.2
- Kubernetes 1.19.6 or release higher
- 1 Node with JupyterLab-JupyterHub and BASH kernel
- active ssh connection between your JupyterLab-JupiterHub host and one of the Kubernetes cluster nodes (for example with the master node)
 Lab Details
Lab Details
This Lab uses Kubernetes,Docker , SQL Server 2019 , Azure Data Studio, SQL Command Line Tools, and the Kubernetes CLI (kubectl).
| Primary Audience: | Administrators looking to learn how to manage Storage with CSI drivers on Kubernetes and Administrators looking to learn how to deploy, use, and manage SQL Server on kubernetes |
| Secondary Audience: | Architects, Developers and IT Pros |
| Type: | Interactif Demonstration |
| Length: | 1 hours |
 Lab Modules
Lab Modules
| Module | Topics |
| 01-Deploying to Kubernetes | Introduction on Container Storage Interface (CSI) Driver for Kubernetes and learn install the HPE CSI driver for MapR |
| 02-Create A Storage Class | Learn to create a Storage Class which will be used to provision persistent volumes |
| 03-Create A Persistent Volume Claim (PVC) | Learn to create a Persistent Volume Claim |
| 04-Deploying SQL Server workload | Learn to deploy SQL Server on Kubernetes Cluster. |
| 05-Kubernetes Deployments 2 | Restore SQL Server Database,Learn the basics of connecting and running queries to a SQL Server container on Kubernetes |
| 06-Kubernetes Deployments 3 | Learn Use the persisted data with SQL Server |
| 07-Kubernetes Deployments 4 | Learn to create Clone Persistent Volume Claim (PVC) and use with SQL Server |
| 08-Kubernetes Deployments 5 | Learn to create volumes Snapshot Persistent Volume Claim (PVC) and use with SQL Server |
| 09-Kubernetes Deployments 6 | Learn to create a Volume expansion and use with SQL Server |
 Terminology
Terminology
Throughout this demonstration we take for example the connection with the user stundent4 but all the configurations apply to any user.
 Setup
Setup
Clone the repository :
$ git clone https://github.com/colussim/HPE-Data-Fabric-Jupyter-playbook.git
$ cd HPE-Data-Fabric-Jupyter-playbook
$- Copy the student4-datafabric-csi-jupyter directory into your JuperterLab environment or into the directory of your JuperterHub user.
- Create the same user used in your JupyterLab-JupyterHub environment on your master node of your kubernetes cluster.
- Generate a ras ssh key for this user.
- Update the authorized_keys file with the public keys (in master node)
- To make kubectl work for your non-root user, run these commands, which are also part of the result of the kubeadm init command:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config - Copy the sql-mapr directory contained in the tudent4-datafabric-csi-server directory of the repository into the home directory of your create user on your master node
 Usage
Usage
Load the Notebook : HPEMAPR-SQL-Intro.ipynb

 Conclusion
Conclusion
As you can see, it is quite easy to set up and use HPE MapR CSI Driver .
This version include all the latest capabilities in the CSI specification :
- Dynamic Provisionning : Parameter Overloading
- Volume Snapshots
- Data Sources : Cloning - Volume Snapshot and Restore
- Volume Expansion
Do not hesitate to contact me for more information
 Resources
Resources
HPE MapR CSI Driver for Kubernetes on GitHub
