Setting up a Kubernetes cluster with Terraform, kubeadm and Weave Net on RedHat Enterprise Linux bare-metal servers
This is a step by step guide on setting up Kubernetes on RedHat Enterprise Linux Server bare-metal environnement. The main reason I worked on this project is that i wanted to automate the deployment of kubernetes clusters on servers already pre-installed in RedHat Enterprise Linux Server® 7.x and 8.x for demo environments. Using Terraform provider along with kubeadm you can have a fully functional Kubernetes cluster in few minutes.
It is true that Terraform is more often used in cloud deployments.I did some tests, putting myself in a customer context. My use case is : i have for exemple 3 servers installed in Redhat Enterprise Linux Server operating system , and I need a kubernetes cluster quickly. With a terraform plan in four minutes our cluster and deployed with 1 master node and 2 workers
Prerequisites
Before you get started, you’ll need to have these things:
- Terraform > 0.13.x
- kubectl installed on the compute that hosts terraform
- A minimum of two servers installed with Centos or RedHat Enterprise (Release : 7.x - 8.x)
- On each servers :
- Generate a ras ssh key.
- Update the authorized_keys file with the public keys
Infra
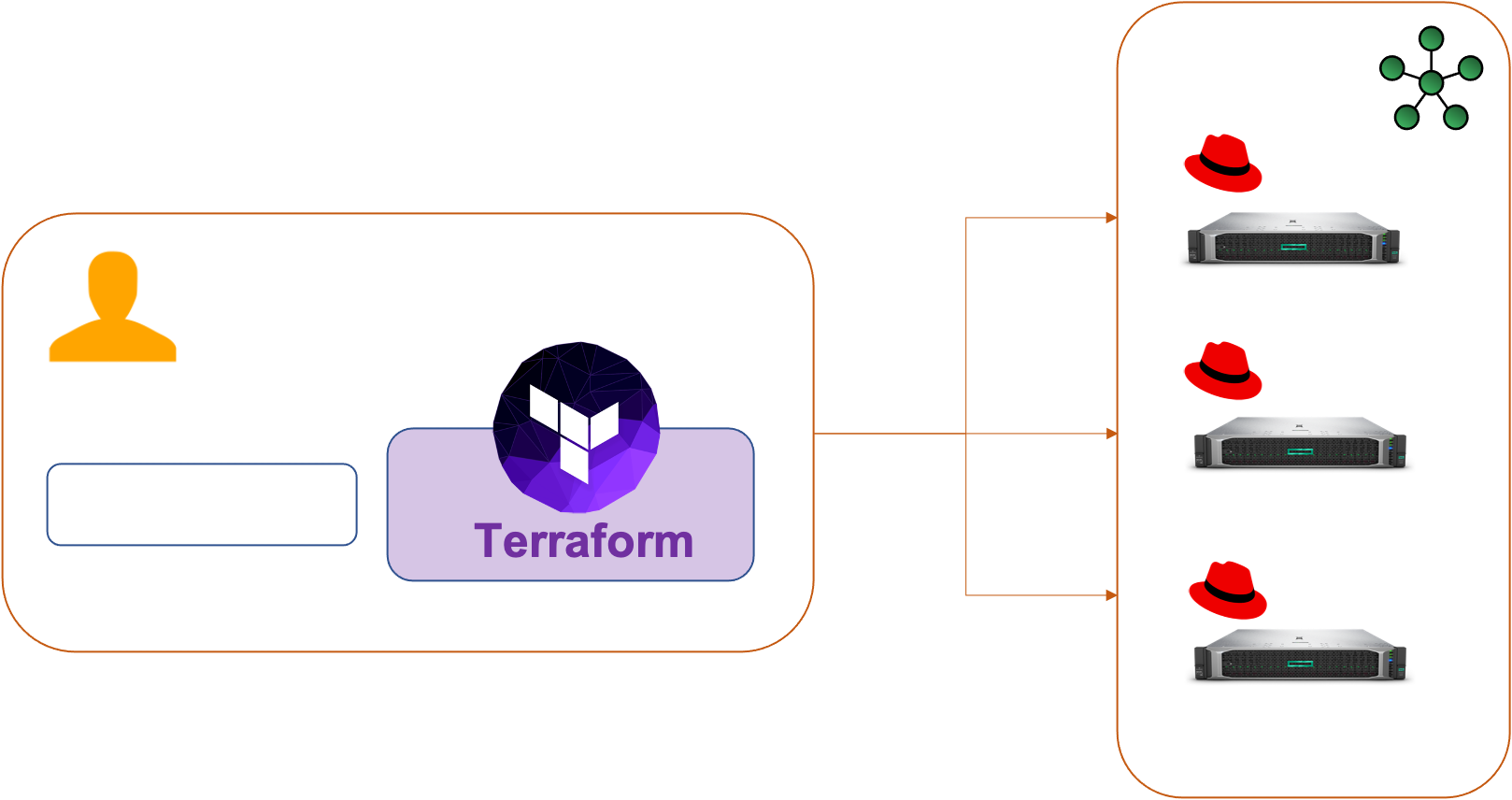
Initial setup
Clone the repository and install the dependencies:
$ git clone https://github.com/colussim/k8sdeploy-terraform.git
$ cd k8sdeploy-terraform
$ terraform initUsage
Create an bare-metal Kubernetes cluster with one master and two nodes:
$ terraform apply \
-var="docker_version=20.10.6-3.el7" \
-var="k8s_version=1.21.0-0.x86_64" \
-var="master=bandol" \
-var='worker=["sauvignon","cabernet"]' \
-var="clustername=epc-eco"If you use the terraform apply command without parameters the default values will be those defined in the variables.tf file.
This will do the following :
- connects to the master server via SSH and installs Docker CE , kubeadm and rpm packages
- runs kubeadm init on the master server and configures kubectl
- installs Weave Net with encrypted overlay
- install cluster add-on (Kubernetes dashboard)
- create a ServiceAccount : admin-user and set authorization
- connects to the workers via SSH and installs Docker CE , kubeadm and rpm packages
- starts the worker nodes
- joins the worker nodes in the cluster using the kubeadm token obtained from the master
Scale up by add hostname or ip address in worker variable
-var='worker=["sauvignon","cabernet","xxxxxxx"]'Tear down the whole Terraform plan with :
$ terraform destroy -forceResources can be destroyed using the terraform destroy command, which is similar to terraform apply but it behaves as if all of the resources have been removed from the configuration.
Remote control
Check if your cluster works:
$ kubectl --kubeconfig $PWD/admin.conf get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
bandol Ready control-plane,master 3d21h v1.21.0
cabernet1 Ready worker 3d21h v1.21.0
sauvignon Ready worker 3d21h v1.21.0To access the dashboard you’ll need to find its cluster IP :
$ kubectl --kubeconfig $PWD/admin.conf -n kubernetes-dashboard get svc --selector=k8s-app=kubernetes-dashboard
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubernetes-dashboard ClusterIP 10.105.212.255 <none> 443/TCP 19hGet token for the connection to the dashboard :
$ kubectl -n kubernetes-dashboard get secret $(kubectl -n kubernetes-dashboard \
get sa/admin-user -o jsonpath="{.secrets[0].name}") \
-o go-template="{.data.token | base64decode}"
eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6Ijd1MlVaQUlJMmdTTERWOENacm9TM0pTQ0FicXoyaDhGbnF5R1
7aM-uyljuv9ahDPkLJKJ0cnen1YDcsswwdIYL3mnW3b1E07zOR99w2d_PM_4jlFXnFt4TvIQ7YY57L
2DDo60vlD1w3lI0z_ogT8sj5Kk1srPE3L6TuIOqWfDSaMNe65gK0j5OJiTO7oEBG5JUgXbwGb8zOK
iPPQNvwrBu6updtqpI1tnU1A4lKzV70GS7pcoqqHMl26D1l0C4-IbZdd1oFJz3XnbTNy70WEMiVp
2O8F1EKCYYpQ
$copy and paste the token value in the dashboard connection window (in next step)
Open a SSH tunnel:
$ ssh -L 8888:10.105.212.255:443 root@bandolNow you can access the dashboard on your computer at http://localhost:8888. Paste the token value :
Conclusion
With kubeadm and Terraform, booting a Kubernetes cluster can be done with a single command and it only takes four minutes to get a fully functional configuration. Improving this guide please submit an issue on GitHub at colussim/k8sdeploy-terraform. Contributions are more than welcome!

