Deploying Microsoft SQL Server 2019 Linux to an Kubernetes Cluster using Terraform
After my previous post about deploying a kubernetes cluster on RedHat Enterprise Linux instances already up, I wanted to deploy SQL Server on this existing kubernetes cluster with Terraform.
Prerequisites
Before you get started, you’ll need to have these things:
- Terraform > 0.13.x
- kubectl installed on the compute that hosts terraform
- One kubernetes cluster
- And the cluster configuration file (/etc/kubernetes/admin.conf)
- My Terraform station is a linux under CentOS, it also works very well under macOS
- Microsoft SQL tools :
- sqlcmd or Azure Data Studio or any other tool that can connect to an MS SQL Server instance
Infra
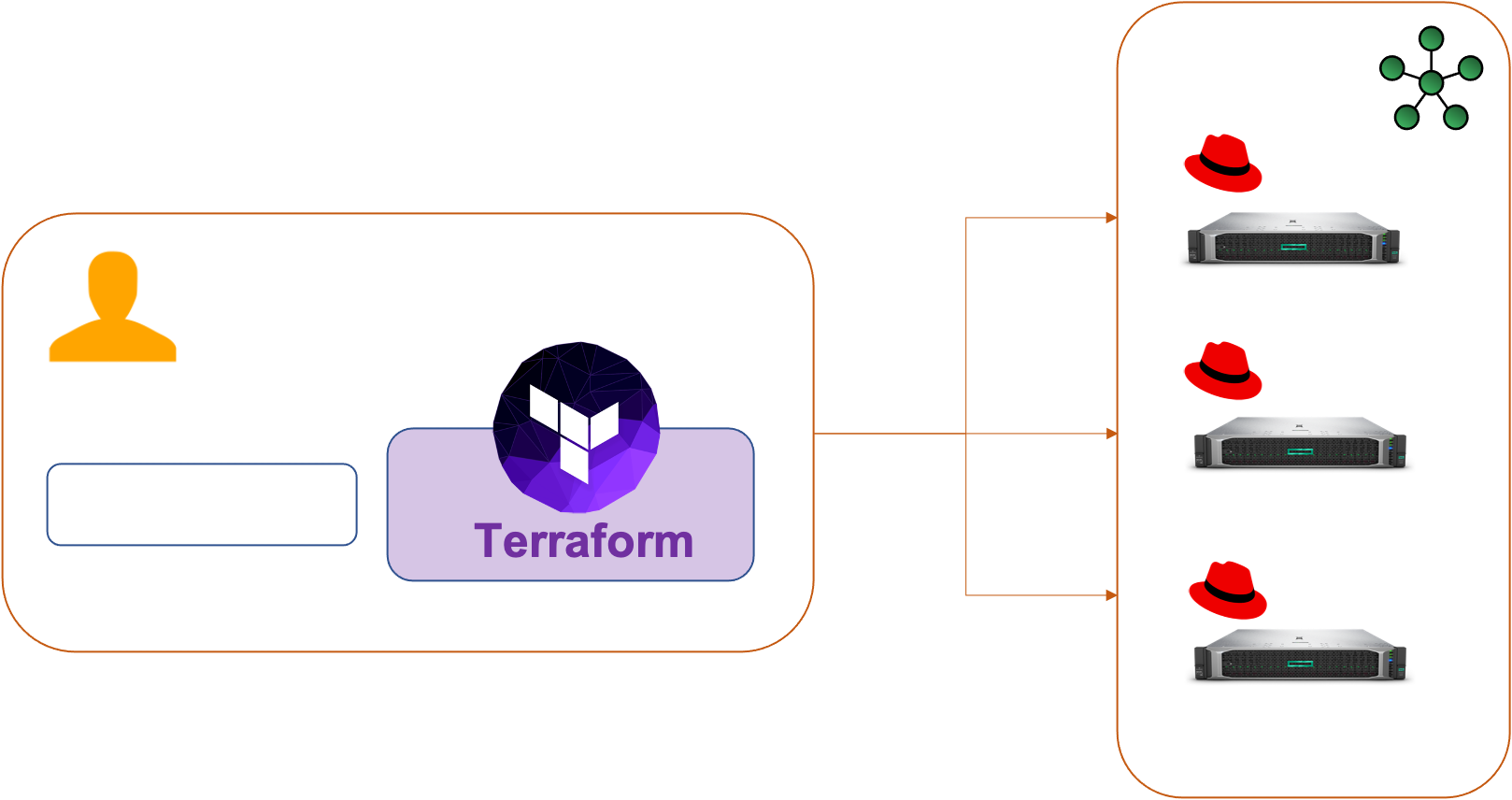
Initial setup
Clone the repository and install the dependencies:
$ git clone https://github.com/colussim/mssqlk8sdeploy-terraform.git
$ cd mssqlk8sdeploy-terraform
$ terraform initUsage
Create a MS SQL Server instance:
$ terraform apply \
-var="name=mssql-deployment-student1" \
-var="namespace=student1" \
-var="pvc=pvc-sql-data01" \
-var="mssql_pvc_size=50Gi" \
-var="mssql_storage_class=sql-sc-1" \
-var="mssql_image_url=mcr.microsoft.com/mssql/rhel/server" \
-var="mssql_image_tag=2019-latest" \
-var="adminpassword=HPeinvent@"If you use the terraform apply command without parameters the default values will be those defined in the variables.tf file.
This will do the following :
- create a namespace
- create of the secret object for the password sa for the MS SQL Server instance
- the password is base64 encoded, in this example the password is : HPeinvent@
- create a PVC : Persistant Volume Claim
- create a deployment object for MS SQL Server : create a MS SQL Server instance
- create a service object for MS SQL Server instance:
Tear down the whole Terraform plan with :
$ terraform destroy -forceResources can be destroyed using the terraform destroy command, which is similar to terraform apply but it behaves as if all of the resources have been removed from the configuration.
Remote control
Check if your SQL Server instance works:
$ kubectl get pods -n student1
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
mssql-deployment-student1-c59f58559-bbbbq 1/1 Running 0 111mTo access the SQL Server Instance you’ll need to find its port map :
$ kubectl get svc -n student1
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
mssql-deployment-student1-service NodePort 10.110.125.206 <none> 1433:31195/TCP 115mIn our deployment for the service we used the NodePort directive and port 1433 is mapped externally to port 31195. We can access our instance by specifying the name (or ip address) of one of the cluster nodes and port 31195.
You can connect to the SQL Server instance outside the Kubernetes cluster with command line :
$ sqlcmd -U sa -P HPeinvent@ -S 10.6.29.166,31195 -q "select @@version"
Microsoft SQL Server 2019 (RTM-CU10) (KB5001090) - 15.0.4123.1 (X64)
Sat 10 2021 18:10:24
Copyright (C) 2019 Microsoft Corporation
Developer Edition (64-bit) on Linux (Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.3 (Ootpa)) <X64>
(1 rows affected)
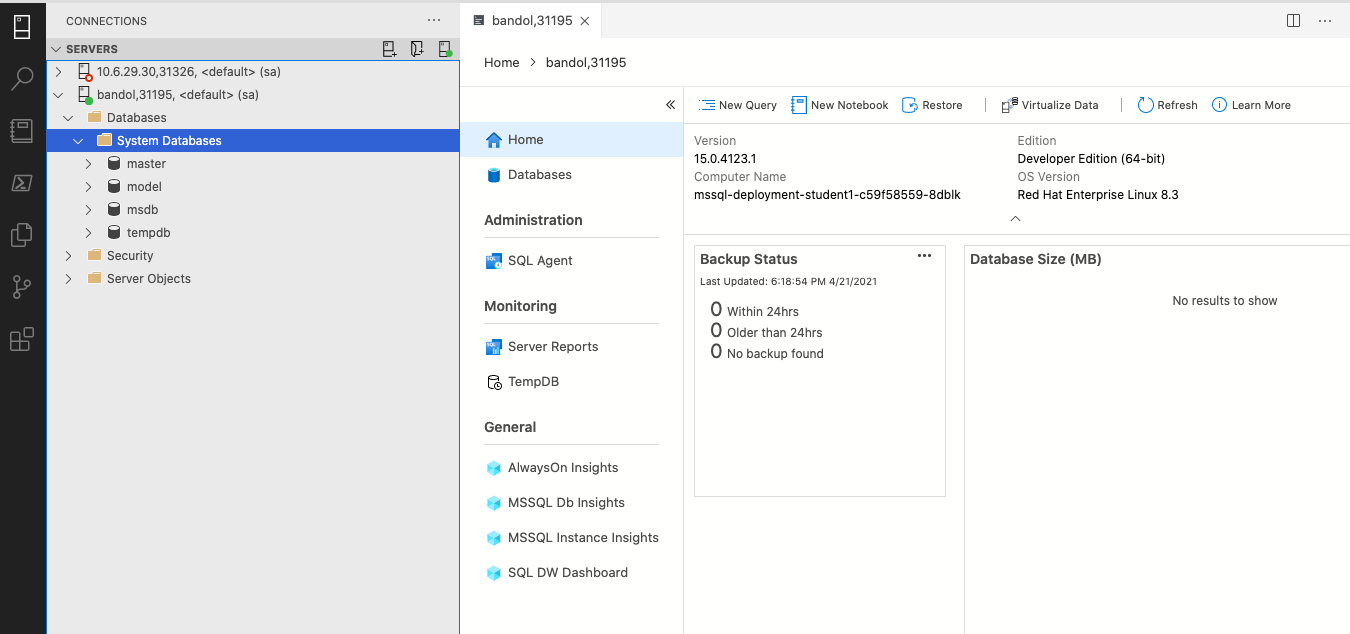
$You can access the MS SQL Server instance with your favorite tool like Azure Data Studio :
Conclusion
Terraform makes it easy to manage Kubernetes clusters and Kubernetes resources effectively. It gives organizations the opportunity to work with infrastructure-as-code, management of platforms, and also the opportunity to create modules for self-service infrastructure. Terraform Kubernetes provider gives organizations all the required tools necessary to manage Kubernetes clusters in the environment.
Improving this guide please submit an issue on GitHub at colussim/mssqlk8sdeploy-terraform. Contributions are more than welcome!

